|
|
Distance between two points in 3-D
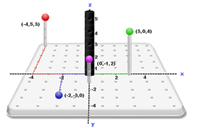
Example: Find the distance between the points (1, 1, 0) and (4, 5, 6).
Solution:
- Find the distance between the points (1, 1, 0) and (4, 5, 6) in the xy plane.
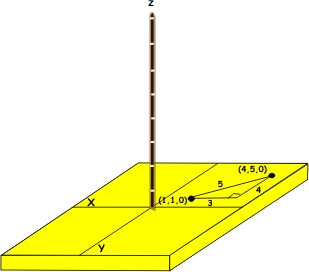
As this problem in two dimensions, Pythagoras' Theorem can be used to show that the distance between
(1, 1, 0) and (4, 5, 0) is equal to 5.
- Find the surface from (4, 5, 0) to (4, 5, 6).
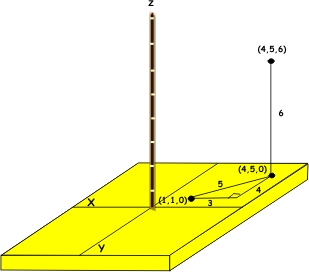
The distance from (4, 5, 0) to (4, 5, 6) is clearly 6.
- Form a right triangle with vertices (1, 1, 0), (4, 5, 0), and (4, 5, 6).
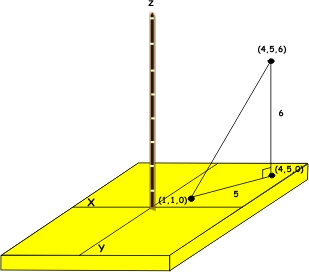
- Use this right triangle and Pythagoras to find the distance between (1, 1, 0) and (4, 5, 0):
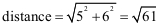
Generalization
To find the distance between two arbitrary points (x1, y1, z1) and (x2, y2, z2), we complete the following steps:
- Find the distance between the points (x1, y1, z1) and (x2, y2, z2) in the plane z = z1.
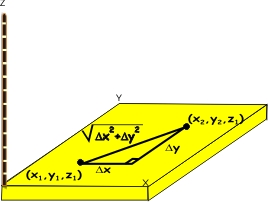
This is a problem in two dimensions so we can use Pythagoras with 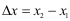 and and 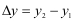 to show that the distance between (x1, y1, z1) and (x2, y2, z2) is to show that the distance between (x1, y1, z1) and (x2, y2, z2) is 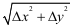
- Draw a line from (x1, y1, z1) to (x2, y2, z2) the distance of which will be
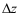 where where 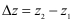 . .
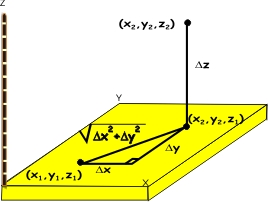
- Form a right triangle with vertices (x1, y1, z1, (x2, y2, z1), and (x2, y2, z2).
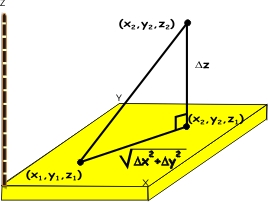
- With this right triangle, we can again use Pythagoras to conclude that the distance from (x1, y1, z1) to
(x2, y2, z2) is 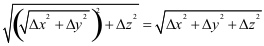 . This is the general formula for the distance between two points in three dimensions. . This is the general formula for the distance between two points in three dimensions.
|
|




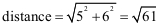

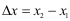 and
and 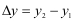 to show that the distance between (x1, y1, z1) and (x2, y2, z2) is
to show that the distance between (x1, y1, z1) and (x2, y2, z2) is 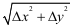
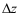 where
where 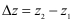 .
.

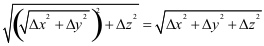 . This is the general formula for the distance between two points in three dimensions.
. This is the general formula for the distance between two points in three dimensions.